In the dynamic and often cutthroat world of business, having a competitive advantage is not just beneficial, it’s absolutely crucial for survival and success. A competitive advantage is the unique factor or set of factors that sets your business apart from the rest of the pack. It’s the special sauce that gives you an edge in the market, the unique combination of attributes that allows you to outperform your rivals and attract customers. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the concept of competitive advantage, discuss the renowned Porter’s competitive advantage framework, and underscore the importance of competitive intelligence in gaining and maintaining an edge in the market.
Understanding Competitive Advantage
At its core, competitive advantage refers to the unique attributes, resources, or capabilities that enable a company to outperform its competitors. It’s the reason why customers choose your products or services over those of your rivals. A competitive advantage could be anything from offering superior quality, lower prices, better customer service, or innovative products. It could also be a unique business model, a strong brand, or proprietary technology.
However, it’s important to note that a competitive advantage is not static. It’s not a one-time achievement that you can rest on. It’s a dynamic attribute that can change, evolve, and even disappear over time as the market evolves, customer preferences change, and competitors up their game. Therefore, it’s crucial to continuously monitor, reassess, and refine your competitive advantage.
Porter’s Competitive Advantage Framework
One of the most widely recognized and utilized frameworks for analyzing competitive advantage is Michael Porter’s Five Forces model. This insightful framework helps businesses understand the competitive forces at play in their industry and identify strategies to gain, maintain, or enhance their competitive advantage. The five forces identified by Porter are:
- Threat of new entrants: This force assesses the ease with which new competitors can enter the market. A high threat of new entrants can erode a company’s competitive advantage, while a low threat can provide an opportunity to maintain or strengthen it. Factors influencing this threat include barriers to entry, such as capital requirements, regulatory constraints, brand loyalty, and access to distribution channels.
- Bargaining power of suppliers: Suppliers who have significant bargaining power can exert pressure on a company by raising prices or reducing the quality of inputs. A company with a strong competitive advantage may be better positioned to negotiate favorable terms with its suppliers. Factors influencing this power include the number of suppliers, the uniqueness of their products or services, and the cost of switching suppliers.
- Bargaining power of buyers: Buyers who have significant bargaining power can demand lower prices or better terms from a company. A company with a competitive advantage may be able to differentiate its products or services to justify higher prices or maintain customer loyalty. Factors influencing this power include the number of buyers, the importance of each individual buyer to the company, and the cost to the buyer of switching to a different supplier.
- Threat of substitute products or services: The availability of substitute products or services can limit a company’s ability to maintain its competitive advantage. Companies must constantly innovate and differentiate their offerings to stay ahead of substitutes. Factors influencing this threat include the relative price and performance of substitutes and the willingness of customers to switch.
- Intensity of competitive rivalry: The level of competition within an industry can impact a company’s competitive advantage. A highly competitive industry may require companies to constantly improve and differentiate their offerings to stay ahead. Factors influencing this intensity include the number of competitors, the rate of industry growth, and the diversity of competitors.
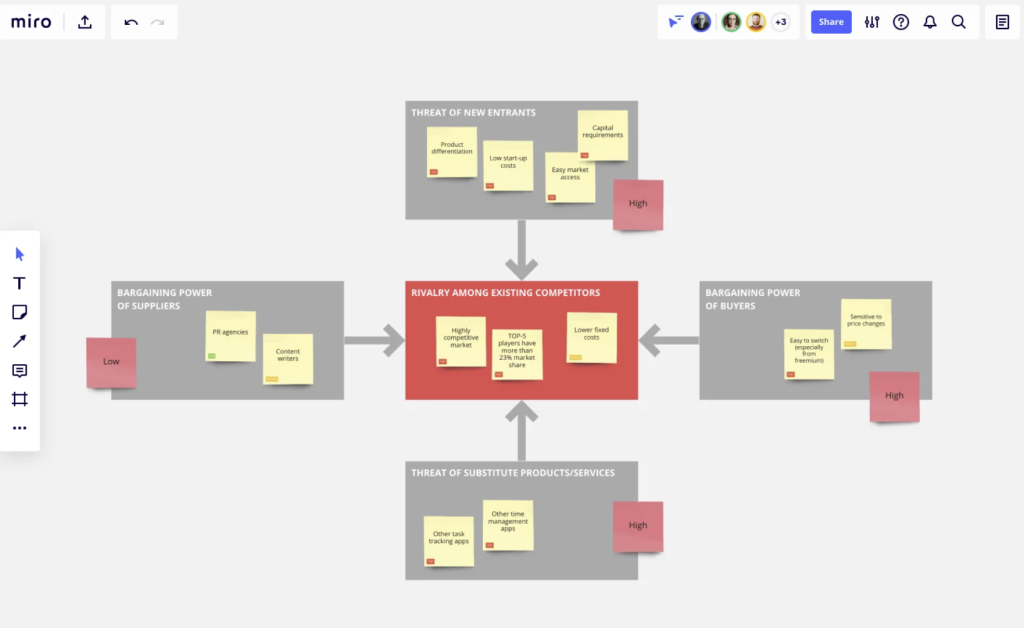
By analyzing these five forces, businesses can identify their competitive advantage and develop strategies to strengthen it. For example, a company facing a high threat of new entrants may focus on building barriers to entry, such as establishing strong brand loyalty, securing patents, or achieving economies of scale.
The Importance of Competitive Intelligence
Competitive intelligence is the systematic process of gathering, analyzing, and managing external information about the competitive environment to assist in achieving company objectives. It involves monitoring competitors’ strategies, products, pricing, and market positioning. Competitive intelligence helps businesses understand their competitors’ strengths and weaknesses, identify emerging trends, and anticipate market changes.
By leveraging competitive intelligence, businesses can identify opportunities to differentiate themselves and gain a competitive advantage. For example, if a competitor is known for its excellent customer service, a business can invest in training its customer service team to provide even better service. Similarly, if a competitor is offering a new innovative product, a business can focus on developing its own unique product to stay ahead.
Competitive intelligence also helps businesses identify potential threats and challenges. By monitoring competitors’ actions, businesses can anticipate competitive moves and develop strategies to counter them. For example, if a competitor is planning to launch a new product, a business can preemptively lower its prices or offer additional features to maintain its market share.
Conclusion
In today’s hyper-competitive market, having a competitive advantage is not just a nice-to-have, it’s a must-have for business success. It’s the unique factor that sets your business apart from the competition, the reason why customers choose you over others. By understanding the concept of competitive advantage, analyzing the competitive forces at play in your industry using Porter’s Five Forces model, and leveraging competitive intelligence, you can identify your unique strengths, develop effective strategies to outperform your rivals, and stay ahead of the game. Remember, a competitive advantage is not static. It requires continuous monitoring, reassessment, and adaptation to stay relevant and effective in the ever-changing market landscape.